
Be it in the form of a family heirloom, an antique piece of jewelry, an engagement or a wedding ring, a diamond is a gem that has symbolized love, legend, and affluence for centuries. But, how much is a diamond worth?
You may think that the price of a diamond is mostly based on the size of the stone. But one thing is for certain: diamond value is not just determined by its carat weight. Much more is involved in determining the price of such valuables. In fact, it’s more complicated than you might think.
It is rare that diamond owners are aware of what precisely makes one diamond more valuable than another. When it comes time to sell a diamond, it is important to understand these differences so that you get a fair deal.
In the following article, we look at what exactly determines the value of a diamond so that you have a fuller understanding of what a diamond you own may be worth in the free market.
The value of diamonds and jewelry are assessed through a process called evaluation. This is essentially a way to place an estimated dollar value on the item. It lets you know approximately what the diamond is worth at current market rates.
Most people think the diamond appraisal is where you find out the value of a diamond. However, an appraisal is not an evaluation. It’s more like a receipt. A professional appraiser is a person who has been trained to examine diamonds and jewelry. They need special credentials, and they’re usually found at private companies or retail stores.
The time it takes to evaluate a diamond’s value varies based on the characteristics of the particular stone. During this time, the gemologist will examine your diamond using special equipment called a gemological microscope. This will allow him or her to see any visual flaws in its cut, color or clarity grades.
After examining your diamond through magnification, the gemologist will determine whether there are any visible signs of damage or wear and tear on the stone and/or its setting. They will also likely do some research to see how much similar diamonds have sold for recently – the current market value of the diamond.
While all diamonds are made of compressed carbon, each individual diamond is unique and different in its own right. Diamonds come in a wide variety of shapes, sizes, colors as well as various internal and external characteristics, which serve as diamond identification. All polished diamonds have some value, but how exactly does one determine how much a diamond is worth?
A diamond’s value is based on a number of various factors. To dispel arguments about a diamond’s worth – the diamond industry professionals use a set of particular guidelines which help establish the exact quality and desirability of a diamond. These guidelines, or the 4 C’s, were established by the Gemological Institute of America and are the basis of diamond value estimation. They include:
Because the diamonds of the world naturally vary in color, clarity and cut, as well as size and carat weight, they will each be valued differently. Let’s now look at each of the 4 C’s more closely.
A major factor in a diamond’s value is its weight. A ‘carat,’ a word derived from carob tree seeds which were used in ancient times to balance scales, is the unit of choice for the weight measurement of a diamond.
One Carat equals 200 milligrams or 0.007055 ounces. The standardized system of metric carats is further divided into 100 points. A 50-point diamond is half of a carat or 0.5 carats.

Much like everything else in the world, the heavier the goods, the higher the price. However, there are various other factors that influence how much a diamond is worth. And these can be even more influential on the final value of the diamond.
Diamonds are available in many colors including blue, pink, yellow, and black. However, the most common color for diamonds is white, or colorless. The more colorless a white diamond is, the more valuable it will be.
A colorless diamond allows easier passage of light. This results in far greater dispersion of light. Or, in layman’s terms: a more sparkly diamond. Diamonds can range from colorless to light yellow, brown, and even gray. And diamonds with identical cut, clarity, and carat weight can have a significant difference in price based on the color alone.
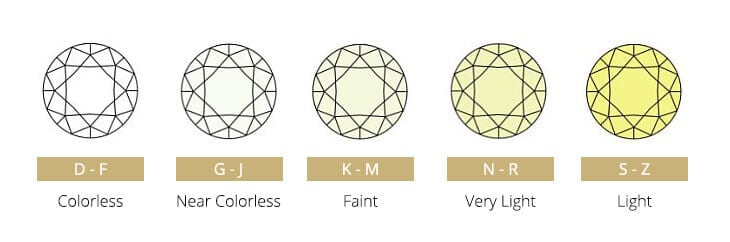
White diamonds are graded from “D” (completely colorless) to “Z” (noticeable color). Colored diamonds (i.e. blue diamonds) have a completely different grading scale where they are actually more valuable the more strongly colored they are.
A diamond is color-graded in a diamond grading laboratory under strictly controlled conditions by comparing the stone to round brilliant diamonds of known color. It is important to know that a diamond’s color grade does not pertain to the face-up surface look of any particular diamond, but rather the body color.
The description of a diamond’s purity is called its Clarity. The amount and location of internal flaws, called inclusions, or external marks, known as blemishes are what determine a diamond’s clarity. The fewer flaws a diamond has, the rarer it is, and the more the diamond is worth.
READ ALSO: Diamond Clarity: Can It Be Identified With the Naked Eye?
All diamonds are systematically graded and plotted under 10X magnification. The clarity grades, assigned by various diamond grading labs, rate the diamonds from being completely flawless to imperfect to the naked eye.
The clarity characteristics, the internal and external flaws of a diamond and their effect on the diamond’s clarity grade, are determined on the basis of five key factors. They include the number, position, nature, size, and color or relief of inclusions and blemishes. Diamonds can range from “IF” (Internally Flawless) to “I3” (Included, Level 3).

Importantly, beyond a certain level of clarity, the naked eye cannot tell the difference between diamonds. But clarity has a significant effect on how diamonds are valued: the greater the clarity, the higher the price.
Clarity is the characteristic of a diamond that sets apart each individual stone, helps separate the imitations from the real deal, and helps provide gemologists and scientists valuable information about the formation of a diamond.
While the diamond’s other Cs are nature-driven, the value and brilliance of a diamond is increased or decreased at the hands of the craftsman who cuts it.
The cut of a diamond is what controls the amount of light reflected through the diamond. The cut is what unleashes the fire and beauty within the diamond itself by allowing the right amount of light to interact with every angle and every facet.
The value of a cut is based on three optical effects it can cause:
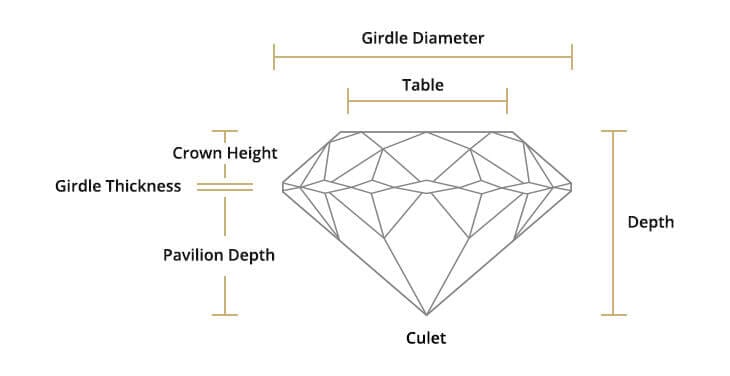
The proportions of a diamond determine how the light performs. The proportions, combined with the polish of a diamond’s surface, affect the overall appeal and beauty of a diamond.

When diamonds are sold as jewelry, two factors come into play. The first is the setting. Many diamond ring settings are meant to make the center stone look much bigger than it is. The second factor is the total carat weight. This refers to the sum carat weight of all diamonds in a ring or piece of jewelry. Large individual diamonds have a much greater value than smaller diamonds that add up to the same total carat weight.
For example, a 2-carat diamond is far more valuable than a ring with small diamonds that add up to a total of 2 carats.
READ ALSO: Does Size Matter? Center Stone Vs. Total Carat Weight
But as stated previously, diamond value is about much more than simply its carat weight. Each of the 4 C’s is extremely important in determining how much a diamond is worth. A 1-carat diamond that is internally flawless, perfectly cut, and “D” color could be worth over $20,000. On the other hand, a diamond of the exact same size and weight that has significant inclusions, has a “good” cut, and a “J” color could be worth under $3,000.
While the diamond industry is known to mostly circle around the 4 C’s – Cut, Clarity, Color and Carat – there is a “fifth C” that is held in equal importance in determining how much a diamond is worth. It is the Diamond Certificate.
Awarded by various grading laboratories established around the world, the Diamond Certificate is the diamond grade assigned to a particular stone after a thorough evaluation. It is a professionally unbiased examination that authenticates the attributes of a diamond. The Diamond Certificate provides a careful validation of the color, carat weight, clarity, along with the exact measurements of the diamond.

Most professional diamond grading labs have their own standards and are known to employ and conform to their own terminology. For any diamond seller, it is imperative to understand the difference between the various grading systems and how they compare to one another. For, a diamond certificate plays a significant part in the value estimation of a diamond.
Some of the most reputable diamond grading laboratories of the world include:
Apart from these top grading labs, there are a plethora of other types of certificates. Each grading laboratory may offer different kinds of certificates or grading reports. They may be highly detailed reports, straightforward dossiers, or more compact certificates. Different grading labs have different names for the certificates they offer which helps distinguish their brands in the diamond industry.
While the AGS is known to call its certificates The Diamond Quality Documents or Diamond Quality Analyses, the GIA refers to them as either a GIA Diamond Report or GIA Diamond Dossier.
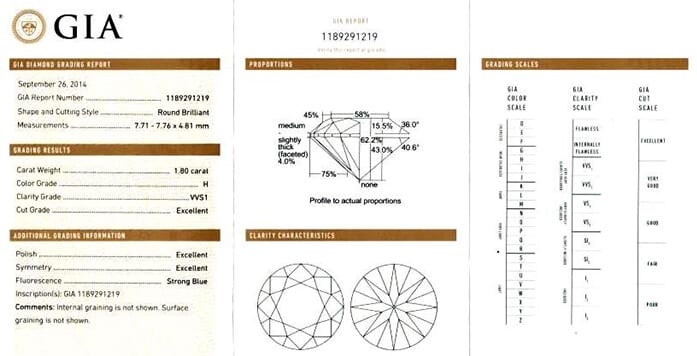
The GSI certificates come in a few different versions, from the very basic Modified Diamond Examination Report, to the most comprehensive one, the Full Diamond Examination Report.
Each certificate differs slightly in terminology, grading system, simplicity, and layout. There are some, which include diagrams or proportion values while others don’t.
Each certification authority has its unique quirks. The GIA is known to be the strictest for Clarity, generally awarding at least one grade lower than other laboratories.
The HRD is known to add its own term of clarity grade to all diamonds with impurities invisible to the 10X magnification; the Loupe Clean.
The AGS clarity grading is quite similar to the GIA while the IGI, EGL, and HRD all award one or two grades higher than the GIA.
READ ALSO: all about the GIA Grading Report
The same holds true for the difference in Color grading by various diamond-grading laboratories. The GIA is the authority while HRD and AGS match closely. EGL, on the other hand, tends to award higher grades than the GIA.
It is important to note that the certificate doesn’t actually alter the value of the diamond – it simply confirms its authenticity and characteristics.
On the one hand, if one laboratory says your diamond’s color is “E” and one says it is “D,” this will have an effect. On the other hand, jewelers generally tend to value GIA certificates more in their reliability.
Apart from the 4 C’s, there are a number of other factors that tell us how to determine diamond value. These factors are not as major though they do have an effect.
The culet is the bottom point of a diamond. Usually slightly flat or faceted, the culet affects the light performance of a diamond. The culet size and angle are two main factors, which can have a significant effect on the value of a diamond.
The ideal culet should be positioned in the exact center of the bottom of the diamond and should be of a small size. Angle deviation and increase in size both adversely affect the diamond’s price.
The thickness of the girdle or the edge that is formed where the top (crown) and the bottom (pavilion) of the diamond meet, could potentially have a negative effect on the value of a diamond. Unequal thickness of the girdle will undermine the symmetry of the diamond, which is essential for light performance.
There is a lot of controversy attached to the effect of laser inscriptions on the value of a diamond. Laser inscription causes microscopic indentations on the surface of the diamond itself, marring it with imperfections.

Therefore, it should have an effect on the clarity of the diamond and thus on the overall price value. However, ironically, as most certification companies inscribe the diamonds themselves, they have the ability to exclude them from the grading altogether.
While laser inscriptions should in theory have a depreciating effect on a diamond’s worth, they sometimes increase the value instead. These laser inscriptions, especially those done by certification companies like the GIA, are taken as validation and proof of the quality of the diamond. Moreover, these laser inscriptions help avoid confusion, determine ownership, as well as deter fraud in the diamond industry.
The Rapaport Report is an industry report created by the Rapaport group and published weekly. This report details the value of diamonds based on all of the above characteristics. Once a diamond’s characteristics have been determined, a jeweler will refer to the Rapaport report to determine the actual price.
The report lists prices per carat (in hundreds) on a matrix of clarity and color. Per-point value of diamonds increases the larger the diamond is. So, a 1.01-carat diamond may cost significantly more than a .99-carat diamond despite the fact that they are almost exactly the same size. (Shopping tip: All things being equal, buy the .99-carat over the 1.00 carat diamond to save significant money.)
Once a price has been determined based on this report, jewelers will make adjustments based on cut, girdle, culet, and other secondary factors.
Finally, jewelers may apply discounts or premiums of a certain percent at their own discretion. Once these are applied, you’ll have the full understanding of how much the diamond is worth on the market.
If you have a valuable diamond engagement or wedding ring that you no longer need or want, it may be time to sell your ring. There are many things you could do with that pile of cash such as:
Even though you now know how much a diamond may be worth based on various criteria, you might decide that now is best the time to sell your ring. However, you may not know where to turn for an evaluation or to get the best value for your gem.
The good news is that this is exactly why Worthy exists! Check out this article on how to sell your engagement ring and or wedding ring learn exactly how to sell your ring for the best price.
©2011-2026 Worthy, Inc. All rights reserved.
Worthy, Inc. operates from 45 W 45th St, 4th Floor New York, NY 10036